|


| The Thermal Mechanical Analyzer (TMA) made by Perkin Elmer is a versatile laboratory instrument. It can be used to measure dimensional and viscoelastic changes as a function of temperature or time. The TMA primarily consists of three components: the LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer), a furnace, and a linear motor for probe loading. The LVDT measures displacement by detecting a change in voltage caused by movement of the probe through a magnetic core. As the probe moves through the core, it causes a change in current in the coil. The displacement is then correlated to the change in voltage. On top of the LVDT is the linear motor, which provides the load for the static force used during the runs. |
 |
 |
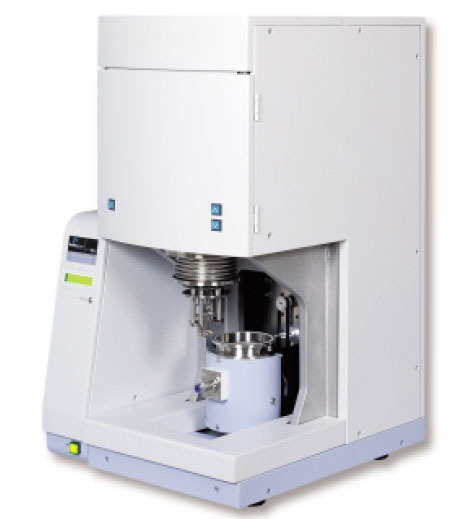
The DSC actually consists of two separate furnaces for the sample and the reference sides. The system can be divided into two control loops, the average temperature loop and the differential temperature loop. The average temperature loop ensures that the sample and reference sides are heating at the programmed rate. The differential temperature loop maintains identical temperatures between the reference and sample pans regardless of the different amount of heat needed to enter the sample side. This process ensures that the sample is always kept at the same temperature of the reference regardless of any changes that occur within the sample requiring more or less heat flow. When an endothermic process occurs such as softening or melting, more heat is added to the sample side relative to the reference to make up for a difference in temperature. With an exothermic process less heat is added to the sample relative to the reference side. |

| This Thermo-Gravimetric Analyzer (TGA) made by Perkin Elmer measures the weight loss of a sample as a function of temperature. This is done by placing a sample into a sample holder that hangs from a micro-gram balance during the entire experiment. The balance mechanism consists of a sample pan holder suspended by a long hang down wire. The hang down wire is connected to the balance lever by a small quartz link to prevent static build up. The weight of the sample holder configuration is electromagnetically balanced on the other side so that the balance can be zeroed before each run. |
 |

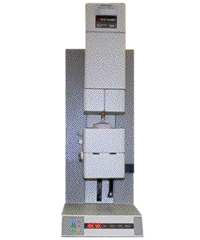 |
The Thermal Mechanical Analyzer (TMA) made by Perkin Elmer is a versatile laboratory instrument. It can be used to measure dimensional and viscoelastic changes as a function of temperature or time. The TMA primarily consists of three components: the LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer), a furnace, and a linear motor for probe loading. The LVDT measures displacement by detecting a change in voltage caused by movement of the probe through a magnetic core. As the probe moves through the core, it causes a change in current in the coil. The displacement is then correlated to the change in voltage. On top of the LVDT is the linear motor, which provides the load for the static force used during the runs. |
|